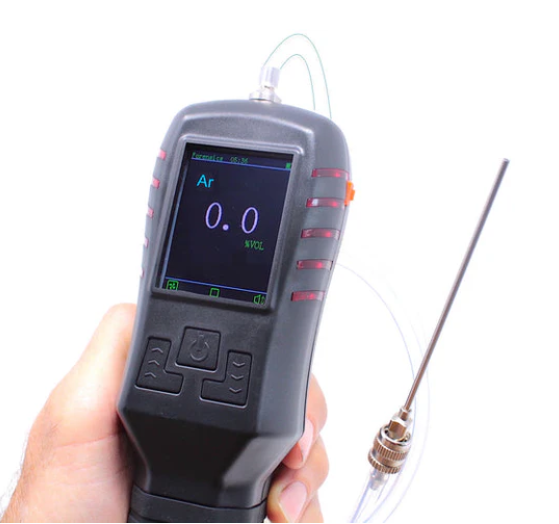
Argon gas detectors are crucial when working with argon, as inhaling dangerous levels of the gas can pose health risks. Argon, an inert noble gas, has various applications due to its unreactive nature, such as protecting weld areas and detecting gas leaks. Argon gas detectors are essential for ensuring the safety of people, particularly welders, who may be exposed to the gas. These detectors continuously monitor the atmosphere, alerting users when argon concentrations reach hazardous levels. Additionally, argon gas detectors play a vital role in identifying gas leaks when argon is used as a tracer gas. Understanding the properties of argon and the importance of gas detection is key to selecting the most suitable argon gas detector for specific applications.
Pros |
Cons |
|
✅ Inert and nonflammable gas ✅ Argon is increasing in popularity due to the limited supply of helium ✅ Argon gas detectors are used to detect argon gas in a welding field or in a gas leak. Other applications include producing metals, preventing erosion, and detecting gas leaks in pressure, vacuum systems. |
⛔ Argon gas detectors are expensive ⛔ Argon is a difficult gas to measure ⛔ Argon may not be used as a tracer gas in all gas leak testing performed ⛔ Argon gas analyzers are a specialized product with little literature or tutorials |
What is the Best Argon Detector?
Some suitable argon gas detectors are available on the market, although they can be difficult to find. Several examples of devices may include the following:
- Forensics Detectors Argon Analyzer
- GasCheck G3 Argon Gas Leak Detector
- Ion Science Argon Gas Leak Detector
- Restek Argon Gas Leak Detector
- AGC Instruments, Argon Gas Leak Detector
What is an Argon Gas Detector?
An argon detector is a piece of detection equipment used to detect the presence of argon gas. Due to its primary use in leak detection, it is mostly available in portable or handheld forms. These forms allow for easy movement of the device which is critical for effective detection of gas leaks.
What is Argon Gas?
Argon gas is colorless and odorless. It does not react with other chemical compounds, meaning it is inert. It has many uses including the following:
- Producing titanium
- Protecting the weld area
- Preventing oxygen from eroding lightbulb filaments
- Detecting leaks
Is Argon Gas Hazardous?
Argon gas can be hazardous at times. In general, argon gas can irritate the skin and eyes if inhaled or encountered.
If it is inhaled in large concentrations, it has the potential to act as an asphyxiant. This can be life-threatening.

How is Argon Gas Used in Leak Detection?
In leak detection, argon gas may be used as a tracer gas. This means that it is introduced to areas where a leak is suspected to be so that a mass spectrometer can measure the leak and alert the user as to the location and size of the leak.
Argon gas can be used in three types of leak detection:
- Vacuum detection
- Pressure detection
- Vacuum-pressure detection
Who Uses Argon Gas Detectors?
Many individuals may find a use for argon gas detectors. The average homeowner likely does not need to purchase an argon gas detector, but some of the following individuals may want to consider it.
Welders
Welders may benefit from having a personal argon gas detector on their person while they are working. While using argon to protect the weld area, they may be unknowingly exposed to higher concentrations of argon gas that can cause bodily harm. A detector can alert welders when the concentration grows too high so they can respond accordingly without risking harm.
Material Production Workers
If argon gas is to be used in the production of certain materials, such as titanium, it could be useful for workers to have an argon gas detector readily available. This will help to protect them from potential harm as they are exposed to argon gas.
Gas Leak Detection Specialists
Gas leak detection specialists require an argon gas detector to be successful. If they are using argon gas as the tracer gas, having a detector capable of measuring the concentration of argon is imperative to identifying the location and size of the leak.

Argon has long been utilized in technological applications, such as inert-gas shielded welding, metallurgy for backing melts, science and medicine as a carrier gas for gas chromatography, and the lamp industry as a filling gas.
Why detect Argon Gas?
There are several scenarios where the detection of argon gas may be necessary. Here are a few examples:
-
Argon Industrial Safety: In industrial settings where argon gas is used or stored, such as welding shops, laboratories, or manufacturing plants, it is essential to monitor the presence of argon to ensure worker safety. Argon is an asphyxiant gas, meaning it can displace oxygen in confined spaces, leading to a lack of breathable air. Gas detectors capable of detecting argon gas are employed to alert workers to the presence of potentially hazardous concentrations.
-
Argon Leak Detection: Argon gas is commonly used in various industries, including the electronics industry, where it is employed as a protective gas for sensitive components or as a tracer gas for leak testing. In such cases, leak detection systems may be used to identify any unintended releases or leaks of argon gas. These systems employ sensors or detectors specifically designed to detect argon and provide early warning of leaks.
-
Argon Analytical Instrumentation: In scientific and analytical laboratories, argon gas is often used as a carrier gas or as a medium for creating controlled atmospheres. Gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, and other analytical instruments may require argon gas. Gas detectors may be employed to verify the presence and purity of argon gas, ensuring accurate and reliable analytical results.
Why is Argon Used in Leak Detection?
Argon gas is used as a tracer gas in leak detection due to:
- Its lack of interference with other argon molecules due to argon's rarity in the atmosphere
- Its properties that make it non-explosive, non-toxic, and unreactive
- Its ability to not contaminate the detector used
CASE STUDY: Dangers of Argon Gas Leaks
In January 2023, Ken Tran, aged 48, and Jonathan Steinke, 24, were discovered unconscious at the Northrop Grumman facility in West Valley. Their deaths were attributed to oxygen displacement caused by argon gas, a substance used in certain industrial processes. According to police and OSHA reports, argon, being denser than air, can be particularly hazardous in confined spaces as it displaces oxygen.
In response to this tragic incident, OSHA conducted an investigation and issued 13 citations to Northrop Grumman, resulting in fines exceeding $172,000. The citations highlighted critical safety lapses: three were for inadequate "respiratory protections," and the remaining ten addressed violations related to "permit-required confined spaces." This enforcement action underscores the importance of stringent safety protocols in industrial settings, particularly when dealing with potentially dangerous gases like argon.

Is Argon used in Fire Extinguishers?
Yes it is.
Argon is used in argon fire extinguishers, and argon leak detectors are needed to determined if these fire extinguishers are leaking.
Argon is a non-combustible gas that can be recovered from the atmosphere. It is recognized as an environmentally beneficial extinguishing agent because it is fully natural. It's colorless, odorless, tasteless, and chemically neutral, so it's safe to use in crowded situations.

What Are Some Common Methods for Argon Leak Testing?
Argon leak testing is typically accomplished through one of three methods: using vacuum techniques, using pressure techniques, or using vacuum-pressure techniques.
Vacuum
In this method, the leak detector is connected to a vacuum pumping system while a pump evacuates the object of interest. A high-pressure vacuum is used to detect a leak using introduced gas.
Pressure
The pressure technique requires the object of interest to contain gas at a higher pressure than that which is present in the atmosphere. Then, a leak detector can be introduced. This technique can be useful for large objects such as tanks.
Vacuum-Pressure
Using this technique, the object of interest has gas introduced to it to give it a certain pressure. Then, it is placed in an evacuation chamber where the detector is connected. This is common in high production testing.
Is Argon Flammable?
Argon is considered non-flammable. It is still important to note that containers of argon may still explode in the event of a fire.
Are Argon Gas Detectors Accurate?
Yes.
An Argon detector should be accurate so long as they are purchased from a reputable manufacturer. Further, to ensure accuracy, make sure the device has been calibrated to NIST traceable gas standards.
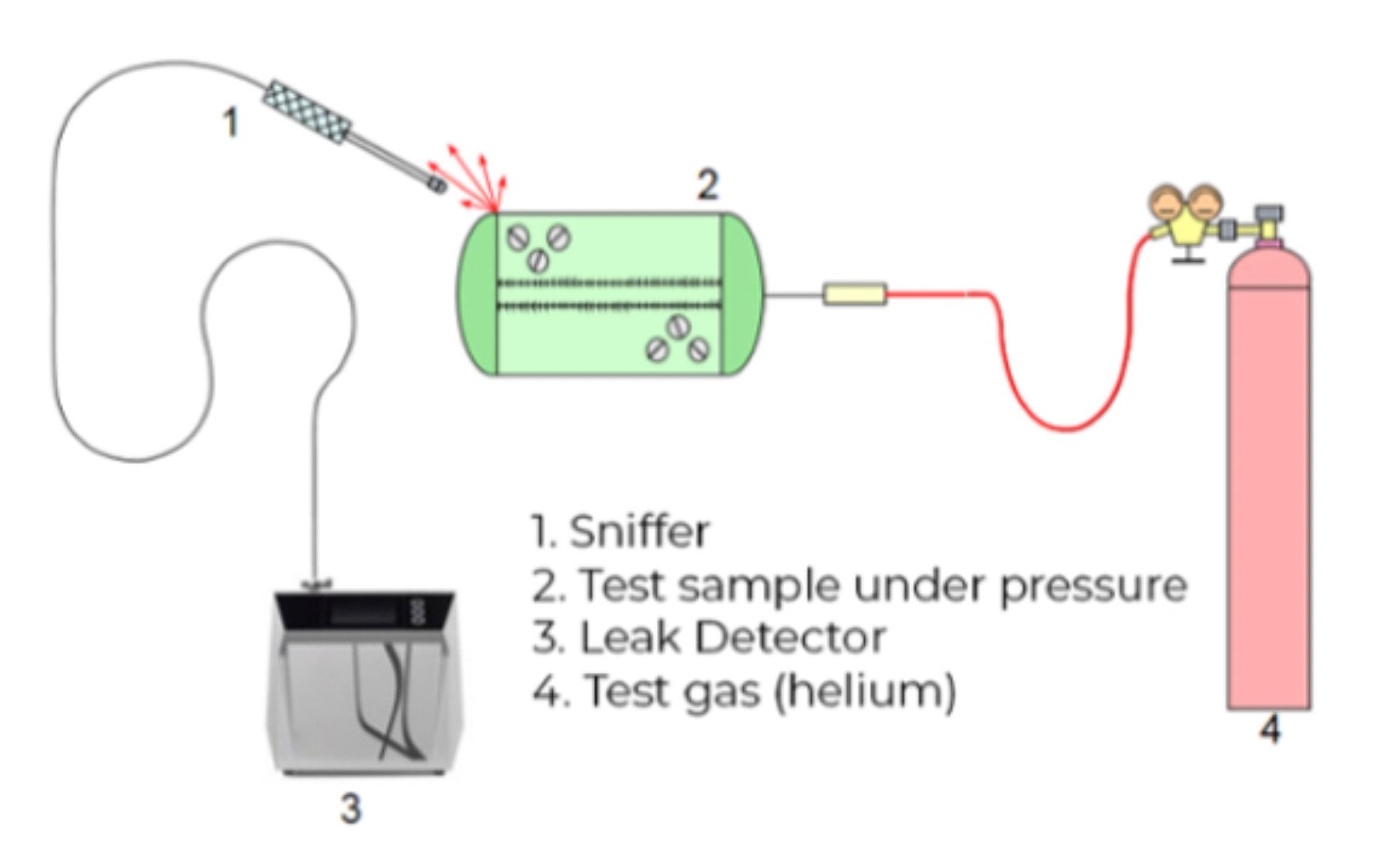
What Kind of Leaks Can Argon Gas Detect?
Argon can be used to detect gas leaks. When argon is used to detect gas leaks, it is used as a tracer gas introduced to a pipe, tank, or another object that has a suspected leak. Then, one of the gas leak detection techniques can be used to discern the location of the gas leak.
Where Should an Argon Detector Be Located?
In most cases, an argon gas detector is location dependant. The user typically probes at different locations with a probe that draws the air to the sensor. In some cases, the sensor can be at the end of a gooseneck and the sensor can directly detect the argon gas via natural diffusion.
How Long Do Argon Gas Detectors Last?
Argon gas detectors employ thermal conductivity sensors (thermistors) that are solid state electronic components which last well over 5 years of operation.
What is Argon Gas Used For?
Argon gas is used for a number of functions. As mentioned, it can be used to protect the weld area. More specifically, argon gas is used for this purpose because it creates an inert atmosphere for the welding to take place where reactions cannot take place. This is important for preventing the oxidation of metals.
Argon gas is also frequently used in gas leak detection. Here, it may be used as a tracer gas since it is not abundant in the atmosphere.
Is Argon used in Welding?
Argon gas is commonly used in welding processes, specifically in gas metal arc welding (GMAW) and gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), also known as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, respectively. Argon is used as a shielding gas to protect the weld area from atmospheric contaminants such as oxygen, nitrogen, and moisture. The argon gas forms a stable shield around the weld, preventing the formation of undesirable oxides and ensuring a high-quality weld. Argon is commonly mixed with other gases like carbon dioxide or oxygen, depending on the specific application and material being welded.
The choice of argon gas as a shielding agent is due to its inert properties. Argon is a noble gas, meaning it is chemically non-reactive and does not readily combine with other elements. This characteristic makes it an ideal choice for welding applications as it doesn't introduce impurities into the weld pool. Additionally, argon has excellent thermal conductivity, which helps dissipate heat during the welding process, preventing distortion and ensuring better control over the weld.
It's worth noting that while argon is commonly used for welding, there are other shielding gases like helium and carbon dioxide that can be utilized.
How Do You Get Argon Gas?
Since argon gas is found in the Earth's atmosphere, it is typically acquired commercially by distilling liquid air. Argon gas supply can also be purchased by Forensics Detectors.
Is Argon Gas Better Than Helium Gas for Leak Testing?
Argon and helium gas are both useful for gas leak detection-- however, they may be used in different instances.
Helium gas is more commonly used, however due to the limited helium supply, argon gas is increasing in popularity.
Can You Smell Argon Leak?
No, argon is an odorless, colorless, and tasteless noble gas. Human olfactory receptors cannot detect its presence, making leak detection equipment essential for safety monitoring.
Final Words
Argon, an inert gas, can pose dangers to humans if improperly inhaled, making gas detection crucial in various applications such as welding and gas leak detection. Argon gas detectors are essential for ensuring the safety of individuals working with this gas, as they continuously monitor the atmosphere and alert users when argon concentrations reach hazardous levels. These detectors employ different techniques and consider various tracer gases to identify leaks effectively. Proper maintenance, including frequent checks to ensure adequate power and functionality, is vital for reliable gas detection. As the use of argon increases due to the limited supply of helium, another inert gas, the importance of argon gas detectors grows accordingly.
About the Author
Dr. Kos Galatsis ("Dr.Koz") is the President of FORENSICS DETECTORS, where the company operates from the scenic Palos Verdes Peninsula in Los Angeles, California. He is a subject matter expert on gas sensor technology, gas detectors, gas meters, and gas analyzers. He has been designing, building, manufacturing, and testing toxic gas detection systems for over 20 years.

Every day is a blessing for Dr. Koz. He loves to help customers solve their unique problems. Dr. Koz also loves spending time with his wife and his three children going to the beach, grilling burgers, and enjoying the outdoors.
Read more about Forensics Detectors here.
Email: drkoz@forensicsdetectors.com
Phone: +1 424-341-3886

