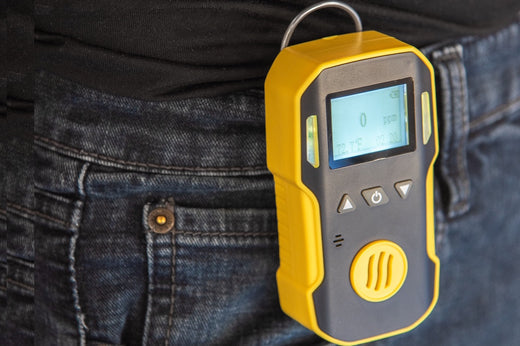
A hydrogen sulfide (H2S) monitor is an important detection device that measures the concentration of H2S gas in the air. These monitors are essential for ensuring personal safety in hazardous environments such as tanks, vessels, silos, pits, manholes, and tunnels, where H2S gas can accumulate to dangerous levels. When unsafe concentrations of hydrogen sulfide are detected, the H2S monitor alerts the user through a combination of audible, visual, and vibration alarms, allowing for immediate action to prevent exposure to this toxic gas. Hydrogen sulfide gas monitors are widely used in various industries, including maritime, oil and gas, construction, mining, water, and wastewater, where the risk of H2S exposure is significant. By providing reliable, real-time detection of hydrogen sulfide gas, these monitors play a vital role in protecting workers' health and safety in these challenging environments.
Pros |
Cons |
|
✅ Small and low-cost detectors available for H2S safety. ✅ H2S can be detected also by the nose "sometimes". ✅ Many H2S monitor models are available for less than $99. |
⛔ H2S smell is deceiving. Different noses have different sensitivities and prone to olfactory fatigue. ⛔ Bump testing and calibration may be forgotten by users. ⛔ Sensors typically last from 24 to 36 months. |
What Is the Best H2S Monitor?
There are many H2S gas monitors on the market. Our favorite and most reputable brands include the following:
- Forensics Detectors H2S Monitors
- MSA H2S Monitor
- Industrial Scientific H2S Monitors
- Honeywell Hydrogen Sulfide Portable Meters
- Macurco H2S Monitor
Top 5 Hydrogen Sulfide Monitor Comparisons?
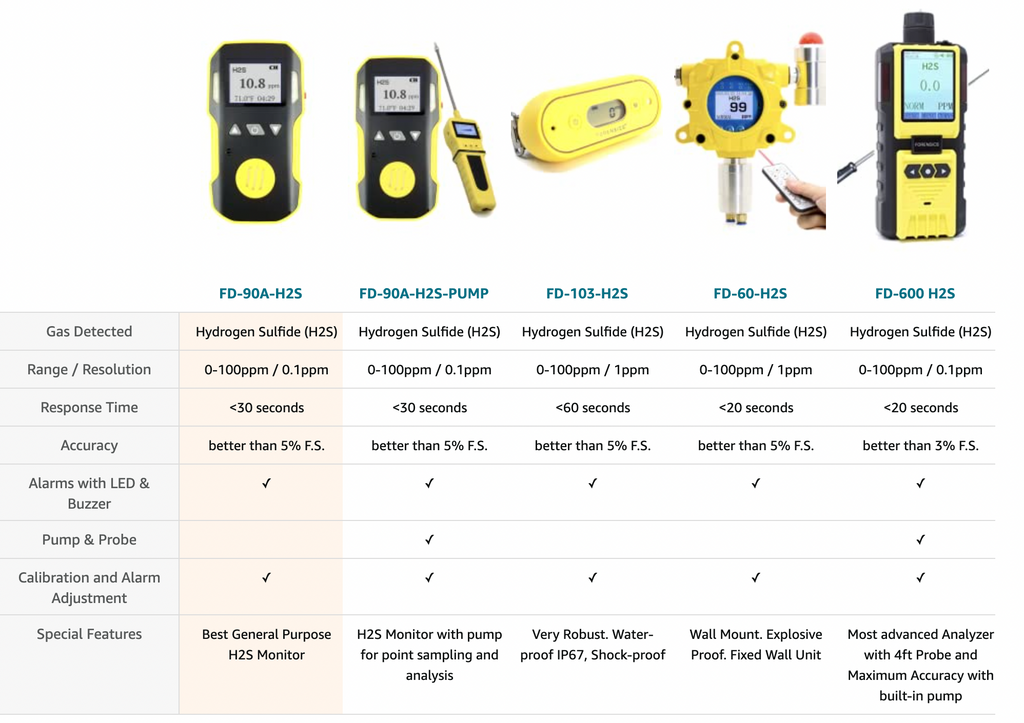
What is a H2S Monitor?
A H2S monitor detects hydrogen sulfide gas concentrations. H2S meters typically have a long-life battery, large screen that displays the parts per million H2S concentration. Some H2S monitors also have LED, vibration, and buzzer alarms.
It should be noted that H2S gas monitors are also called hydrogen sulfide meters, hydrogen sulfide detectors, H2S meter, and H2S gas detectors. These names all refer to the same device, an H2S gas monitor.
What Does an H2S Monitor Detect?
An H2S monitor detects hydrogen sulfide gas in the air and displays levels in parts per million (ppm).
What Is Hydrogen Sulfide Gas?
As a toxic gas, hydrogen sulfide is one of the leading causes of workplace gas inhalation deaths in the United States. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports that H2S caused 60 worker deaths between 2001 and 2010.
Hydrogen sulfide gas may be present in well water, sewers, manure pits, oil and gas wells, and volcanoes.
H2S is heavier than air, so it tends to collect in enclosed areas. These confined spaces include utility holes, sewers, and underground telephone vaults. Its presence makes work in these tight areas potentially dangerous. Therefore, it is imperative to detect H2S gas in such precarious situations.
CASE STUDY: H2S GAS EXPOSURE
People can be exposed to H2S gas in a variety of settings, including industrial, agricultural, and natural environments.
- In industrial settings, H2S gas can be released during the production of petroleum, natural gas, and other chemicals. Workers in the oil and gas industry, chemical plants, and other industrial settings may be at risk of exposure to H2S gas.
- In agricultural settings, H2S gas can be produced during the decomposition of manure and other organic matter. Workers in livestock operations, such as dairy farms and hog farms, may be at risk of exposure to H2S gas.
- In natural environments, H2S gas can be found in geothermal areas, such as hot springs and volcanic regions. It can also be produced by bacteria in swamps, marshes, and other wetlands.
- In confined spaces such as sewers, tanks, and pits, where organic matter is decomposing. Workers who enter these spaces without proper safety equipment are at risk of exposure to H2S gas.
Is Hydrogen Sulfide Gas Dangerous?
H2S is a dangerous gas and can affect human health even at low concentrations. Health effects range from headaches and eye irritation to unconsciousness and even death.
What Does an H2S Monitor Do?
The primary purpose of an H2S monitor is to protect the user from hazardous air quality environments. The H2S monitor warns the user to unsafe air quality via audible, visual, and vibration alarms.
Can I Smell H2S Gas? (Rotten Egg Smell)
Yes, you can smell H2S.
It is that rotten egg smell that is sometimes offensive to people. Some people are very sensitive to it, while others are not. Therefore, it is a bad idea to depend on your nose to determine H2S "potency." Using your nose as an indicator is unreliable as the nose becomes less sensitive the more you smell H2S gas.
This is known as olfactory fatigue. When the nose has odor fatigue and adapts, you become blind to the odor. This also happens for other "aromatic" gases, such as ozone. Your nose is less able to smell the aroma after a prolonged period of exposure.
According to OSHA, humans start to smell H2S gas at levels as low as 0.01ppm. These levels are much lower than a typical H2S monitor can detect. This explains why sometimes we receive customer calls that go something like this - "Why doesn't my H2S detector work?... I can smell H2S gas, but the detector still reads 0.0ppm."
What Are the Different Types of H2S Monitors?
H2S Monitor for Personal ProtectionThe majority of H2S gas monitors are portable. These are small battery-powered units with an H2S sensor that can be clipped to you and provide continuous personal protection with LED, buzzer, and vibration alarms.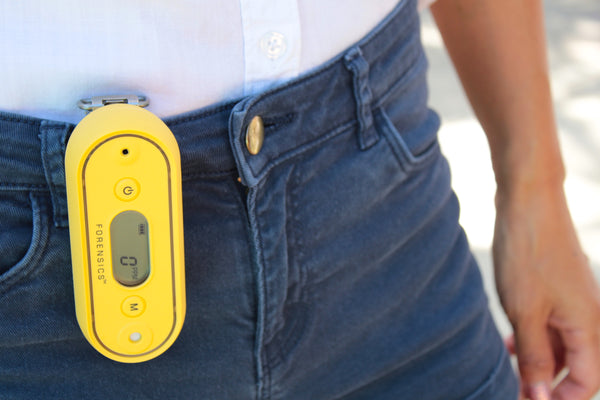  |
H2S Monitor with pump for Point SamplingThis is an H2S gas monitor with a built-in pump or an external pump for point sampling. Before entering a confined space, a sample can drawn while the user remains in a safe location.  |
H2S Monitor for Stationary Fixed WallWall-mounted units provide continuous protection. These devices are more expensive and offer protection in an industrial facility or confined space with heavy occupational traffic, such as a mining shaft. 
|
How Does an H2S Gas Sensor Work?
An H2S gas monitor is composed of electronics and an H2S sensor. The gas sensor converts the gas concentration to an electronic signal for analysis by the onboard microprocessor. From there, the processor outputs the reading to the display. If the readings exceed the pre-set values, the alarms will be triggered to warn the user.
Gas |
Sensor Technology |
Pros |
Cons |
|
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) |
Electrochemical Sensors The gas reacts with a working electrode, triggering an electrochemical redox reaction. A current is generated proportional to gas levels. |
|
|
What Are Safe Hydrogen Sulfide Levels?
Various government agencies have suggested gas exposure limits. Below are some examples of H2S gas exposure recommendations.
Agency |
Recommendation / Requirement |
|
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) |
NIOSH Recommended Exposure Limit (REL): 10 ppm, 10-minute ceiling |
|
Occupational Safety and Health (OSHA) |
10 ppm average over 8 hours |
|
American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) |
1 ppm average over 8 hours 5 ppm average over 1 hour |
What Is an H2S Monitor Used For?
Hydrogen sulfide is produced from organic matter that decays and releases the gas into the atmosphere. Unsurprisingly, it is found in sewage, liquid manure, and other natural places such as sulfur hot springs.
It is also used in manufacturing and industrial processes such as:
- Oil and gas industry
- Sewer and wastewater
- Agricultural silos and pits
- Textile manufacturing
- Pulp & paper processing
- Food processing
Water and Sewer Industries
Workers can be exposed when sterilizing and cleaning. Maintenance of confined spaces in sewers can pose a threat, especially when in manholes, sewer pipes, and septic tanks. Testing tanks before entering using an H2S monitor with pump and probe is essential. When entering confined areas, workers should also wear a personal protection H2S monitor.
Farmers and Agriculture
H2S exposure can also be a problem for farmers when cleaning manure storage tanks or around pit locations. Most often, these are open pits, so personal protection is essential. In fact, manure pits include other toxic gases such as methane, ammonia, and carbon dioxide. Often overlooked, H2S is one of the leading causes of workplace gas inhalation deaths in the USA, killing about 6 people per year.
Oil and Gas Industry
Workers in the oil and gas industry may be exposed to H2S gas. It is a by-product of the desulfurization process. See OSHA Oil and Gas Well Drilling and Servicing.
Industrial Processes
H2S gas is often used or created as a by-product of many industrial process. In this case, a fixed wall gas monitor should be placed in the indoor area to protect workers. These units can also be connected to ventilation fans and turn them ON to reduce the H2S exposure level.

Can an H2S Monitor Be Used to Detect a Sewer Gas Leak?
Maybe.
We do not recommend using an H2S meter for suspected gas leaks in a pipe, joint, or appliance. As a first step, it is better and more cost-effective to use a gas leak detector with gooseneck, semiconducting metal oxide sensor, and reading in ppm. See here.
How Do I Select an H2S Monitor?
To select the best H2S gas monitor that serves your purpose, follow this guide. Start by thinking about these questions to narrow down your selection:
- Do I need a built-in pump or probe with the unit? Do I need to point sample or am I using it for personal protection?
- How often will I use it (to help determine battery capacity)?
- What is my budget and operating cost budget?
- Do I need advanced functions, such as data-logging or Bluetooth?
- Do I need specific accreditations with the monitor, such as ATEX or a NIST traceability calibration certificate?
- Do I require a belt clip for attaching to my clothes?
- Do I need after-sales support, USA headquarters, or fast calibration service?
- Am I using the device for research or personal protection where ppm sensitivity is required?
What Is an H2S Detector, H2S Meter, H2S Sniffer?
These all refer to the same thing. Similar to an H2S gas monitor, these units are sometimes referred to as H2S meters, H2S monitors, H2S detectors, hydrogen sulfide sniffers, hydrogen sulfide analyzers. In the UK, it is called an H2S analyser.
These are names used to describe the same item, a gas measuring device that detects H2S in the air.
How Long Does a H2S Sensor Last For?
H2S monitors typically incorporate electrochemical cell technology. These sensors usually last between 24 to 36 months.
How Do I Test My H2S Monitor?
The best way to test your H2S gas monitor is to expose it to a known gas source. Generally referred to as bump testing, this practice should be performed daily, especially in personal protection applications where safety is paramount - more about bump testing in the next section.
What Is H2S Monitor Bump Testing?
- Bump testing is a procedure where one exposes the detector to a small amount of “blast” target gas to ensure the detector operates and alarms as programmed.
- The function of this test is to verify proper operation and build user confidence, particularly in hazardous applications.
- It is recommended to bump test when first purchased, followed by weekly tests. If using in LIFE-THREATENING and / or DANGEROUS applications, bump test daily.
- H2S bump test gas can be found here.
What Is H2S Monitor Gas Calibration?
H2S gas monitor calibration is the technical task of adjusting the detector to a more accurate reading. This is important because the sensors may drift and degrade over time. We typically suggest calibrating your H2S gas monitor every 6 to 12 months, a typical time period for gas detectors.
Gas calibration is a technical task and requires certain key pieces of equipment. This includes a calibration gas bottle, gas regulator, tubing, and calibration cap fitting. You need to confirm the recommended calibration gas concentration levels with the manufacturer. For the Forensics Detectors H2S gas monitors, we recommend gas calibration with H2S gas at 25 ppm. See H2S calibration gas here.
Be attentive and calibrate daily if:
- The device is used as an analytical tool where accuracy is paramount.
- The device is used in an extreme environment (temp and humidity extremes create sensor drift).
- The user is performing an imminently dangerous or extreme application.
- Bump testing fails. In this case, you must calibrate to make sure the sensors and monitor can alarm.
- The H2S gas detector alarms in the fresh air where a sensor has potentially drifted past a set-point.
Calibration and bump testing are mandatory since imminent injury or death will occur if the device fails. Take it very seriously.
Also, it is important to have a calibration schedule that the owner or employees strictly follow. See gas calibration here.
How Do I Properly Use an H2S Gas Monitor?
When operating an H2S gas monitor, there are some important tips to consider. Be smart, read your product manual, and keep these tips in mind:
- Turn ON the H2S gas monitor in fresh air.
- Ensure the H2S gas monitor is within its calibration period.
- Ensure the H2S gas monitor has been bump tested and validated as operational.
- Check the alarm set-points. Set your alarms as desired.
- If performing analytical measurements, keep the unit stationary. Ensure humidity and temperature are also tracked and remain as constant as possible.
- If using a pump, turning the pump ON/OFF will change the pressure and may affect readings. Take data point readings when the pump is either off or on after 60 seconds, so no erroneous data points are taken due to "pressure change."
What Is the Difference Between ppm and %vol Detector Readings?
A typical H2S gas monitor presents hydrogen sulfide readings in ppm, or parts per million.
The typical scale of concentration for any gas is %vol. The refers to the percentage of the air volume taken up by the gas in volumetric measure. There are other measures based on weight and mols, but this is not important as gas detection primarily involves readings on a volumetric basis.
The part per million (ppm) scale has a direct conversion from %vol.
For example, 100 ppm = 0.01%.
Usually, when the ppm value enters the 1,000 ppm range, it is customary to start using %vol, as it is easier to say 1.1% vol instead of 11,000 ppm.
Conversion Example
H2S % value = (H2S ppm / 1,000,000) x 100%
For example, if we have 5,000 ppm of H2S, then we obtain:
H2S % value = (5,000 / 1,000,000) x 100%
H2S % value = 0.5%
Quick Conversion from ppm to %vol
200 ppm = 0.02%
2,000 ppm = 0.2%
20,000 ppm =2%
200,000 ppm =20%
2,000,000 ppm =200%
Is H2S Explosive?
Yes, it is but must be at higher concentration levels.
The lower explosive limit (LEL) of H2S is 4.3% - this means it is too lean to burn. The upper explosive limit (UEL) is 46% - this means it is too rich to burn.
An H2S fire produces sulfur dioxide which is very toxic.
What Is the Difference Between ppm and %LEL Detector Readings?
It is most common to detect H2S gas using the ppm range due to its low-level health effects. Using %LEL to measure H2S gas is uncommon.
%LEL represents a percentage of the lower explosive limit of the H2S gas. It can be difficult to understand, so follow along with the examples below slowly.
Each combustible gas, such as H2S, has a different explosive limit in air and therefore a different lower explosive level (LEL).
As mentioned previously, H2S gas will explode in air at 4.3% volume (which is 43,000 ppm). This is known as the 100% Lower Explosive Limit. Therefore, 100% LEL = 4.3% volume. When H2S concentration levels reach 100% LEL, it will explode if an ignition source is present. To illustrate with another gas, let's consider propane. For propane, 100% LEL = 2.1% volume, and for hydrogen, 100% LEL = 4.0% volume.
The %LEL scale is based on explosive limits. Each gas, as you can imagine, has different explosive limits. Below is a figure showing the range of LEL and UEL for methane.

What is H2S Olfactory Fatigue?
H2S gas olfactory fatigue, also known as hydrogen sulfide olfactory fatigue, is a phenomenon where a person's sense of smell becomes desensitized to the smell of hydrogen sulfide gas after prolonged exposure. This can occur because the olfactory receptors in the nose become less responsive to the gas over time. As a result, the person may no longer be able to detect the odor of the gas, which can be dangerous as hydrogen sulfide is a toxic gas that can cause health problems or even death in high concentrations. Therefore, it is important to take precautions and use proper safety equipment when working with or around hydrogen sulfide gas.
Can You Smell Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)?
Yes, hydrogen sulfide has a distinctive "rotten egg" odor that humans can detect at very low concentrations. However, at higher concentrations, H2S can quickly overwhelm and deaden your sense of smell, making it particularly dangerous.
Final Words
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a highly toxic gas, and the use of an H2S gas monitor is crucial for ensuring safety in environments where this hazardous gas may be present. H2S monitors are primarily employed for personal protection in confined spaces such as tanks, vessels, silos, pits, manholes, and tunnels, where hydrogen sulfide can accumulate to dangerous levels. When an H2S monitor detects unsafe concentrations of the gas, it immediately alerts the user through a combination of audible, visual, and vibration alarms, enabling them to take swift action to avoid exposure. Industries such as maritime, oil and gas, construction, mining, water, and wastewater heavily rely on hydrogen sulfide gas monitors to protect their workers from the severe health risks associated with H2S exposure. The use of these gas detection devices is essential for maintaining a safe working environment and preventing potentially fatal incidents related to hydrogen sulfide inhalation.
About The AuthorDr. Kos Galatsis ("Dr.Koz") is the President of FORENSICS DETECTORS, where the company operates from the scenic Palos Verdes Peninsula in Los Angeles, California. He is a subject matter expert on gas sensor technology, gas detectors, gas meters, and gas analyzers. He has been designing, building, manufacturing, and testing toxic gas detection systems for over 20 years. 
Every day is a blessing for Dr. Koz. He loves to help customers solve their unique problems. Dr. Koz also loves spending time with his wife and his three children going to the beach, grilling burgers, and enjoying the outdoors. Read more about Forensics Detectors here. Email: drkoz@forensicsdetectors.com
|